Scenario introduction
The scenario
Your workshop drops you into an example development team, at the start of their journey through the DevSecOps world.
They already use infrastructure as code (IaC) to define their environments. Their deployment target is a Kubernetes cluster, which is already set up.
Their continuous deployment (CD) tool is ArgoCD, which is configured to take any changes to in their main infrastructure GitHub branch and apply those changes to the cluster, for both the Prod and Dev environments.
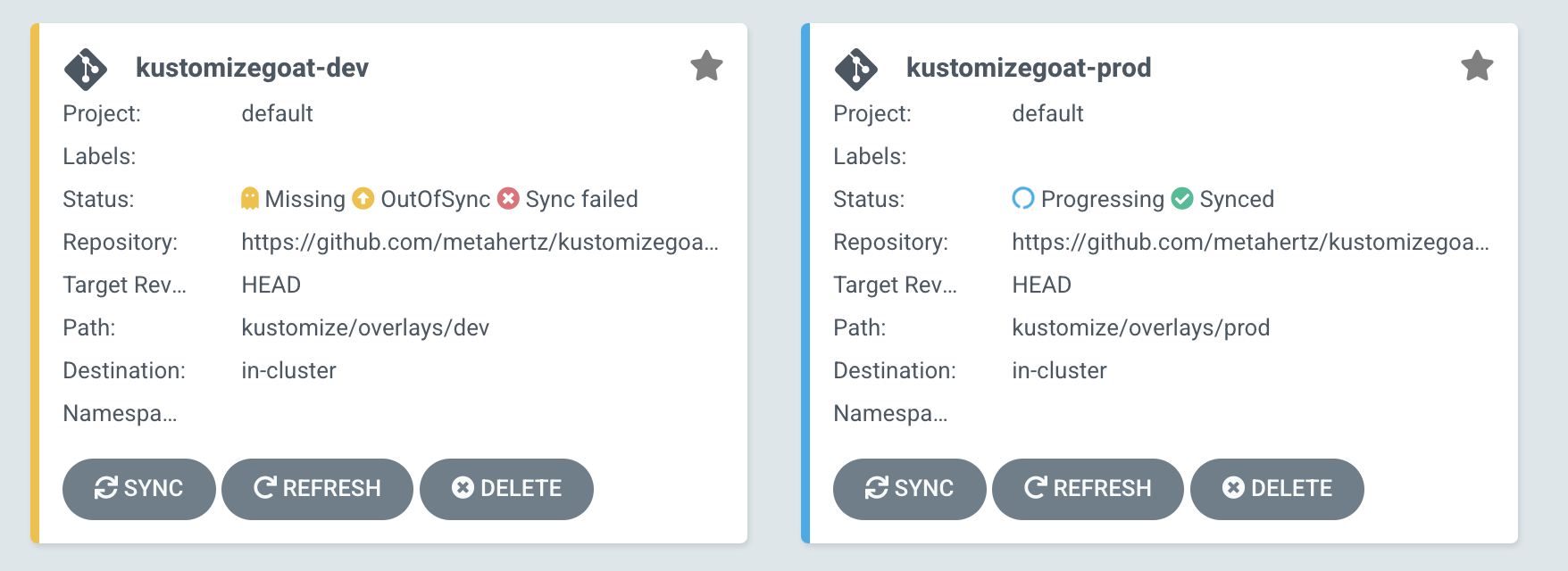
The KustomizeGoat repository we forked during the workshop setup is the repository holding these deployments. Your fork powers these deployments into your cluster, which allows you to make your own changes as we go through this workshop.
Let’s take a look around
kubectl
You should already have access to your kind Kubernetes cluster for this workshop. Confirm your access with the following command showing our Kubenetes cluster nodes:
kubectl get nodes

We can also take a look at the existing namespaces running on our cluster:
kubectl get ns
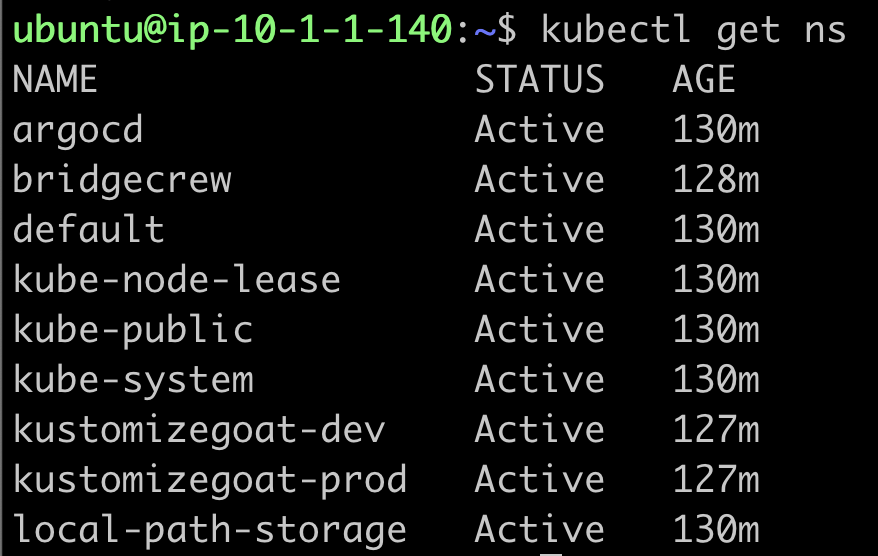
Here we can see a number of namespaces, including one for our ArgoCD continuous deployment system. ArgoCD itself is running on our cluster and monitoring our Git repo for changes to our infrastructure configuration.
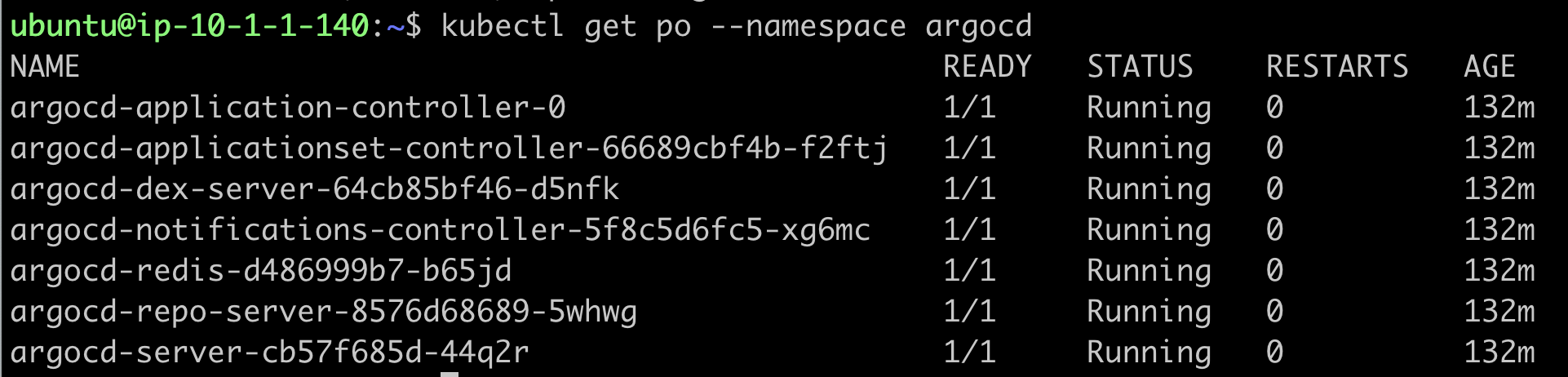
Let’s take a look at the pods and services in that namespace.
kubectl get po --namespace argocd
Now that ArgoCD is up and running, let’s have a look at the relevant services:
kubectl get svc --namespace argocd
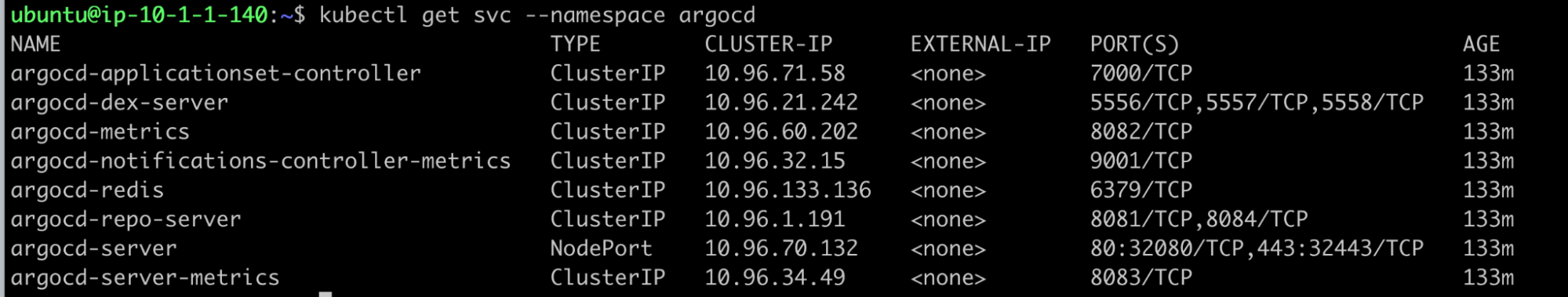
We can see that the web interface “argocd-server” has a NodePort configuration, which means we can use the public IP of our kind host on either HTTP port 32080 or HTTPS port 32443 to access the interface.
In the next step, we’ll explore the ArgoCD setup.